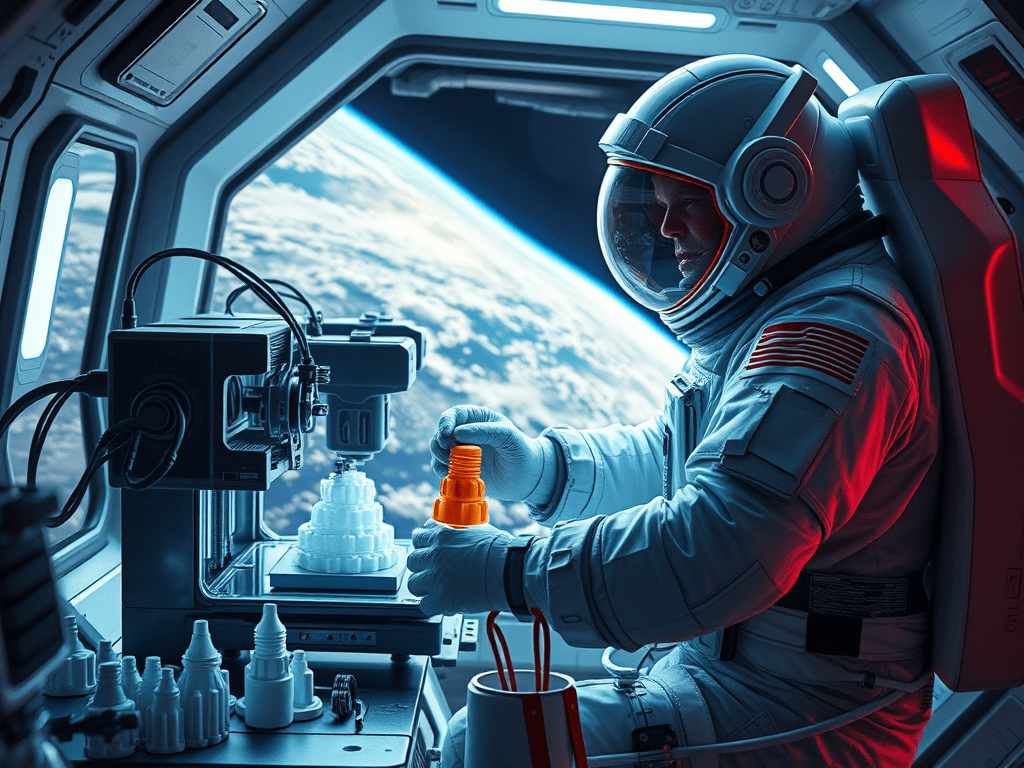
Imagine astronauts printing tools, spare parts, or even habitats—right in orbit or on the Moon. What once sounded like science fiction is now becoming a cornerstone of modern space missions. Welcome to the era of 3D printing in space, where innovation defies gravity.
🌌 Why Print in Space?
Launching every nut and bolt from Earth is expensive and logistically complex. A single kilogram of cargo can cost thousands of pounds to send into orbit. 3D printing offers a game-changing solution: manufacture on demand, using materials already in space or brought in bulk.
Key Benefits:
- Reduced launch weight and cost
- On-demand manufacturing of tools and parts
- Enhanced mission flexibility and autonomy
- Potential use of extra-terrestrial materials (like lunar regolith)
🛠️ From Wrenches to Moon Bases
NASA and ESA have already tested 3D printers aboard the International Space Station (ISS). In 2014, the first tool—a simple wrench—was printed in microgravity. Since then, astronauts have produced dozens of components without waiting for resupply missions.
But the vision goes far beyond tools. Future missions aim to:
- Print habitats on the Moon or Mars using local soil
- Create medical devices tailored to astronauts’ needs
- Build solar panels and antennas directly in orbit
🧪 Materials That Work in Microgravity
Printing in space isn’t just about bringing a printer—it’s about adapting to a hostile environment. Microgravity affects how materials behave, so engineers are experimenting with:
- Thermoplastics like ABS and PEI
- Metal powders for sintering in zero-G
- Biomaterials for tissue engineering and medical use
Some companies are even exploring recycling waste plastic into printable filament, turning trash into treasure aboard spacecraft.
🌍 Earth Benefits from Space Innovation
The tech developed for space printing is already influencing Earth-based industries:
- Disaster relief: Portable printers for remote areas
- Construction: Robotic printers for sustainable housing
- Healthcare: Bioprinting tissues and organs
Space pushes the limits of innovation—and those breakthroughs often come back down to benefit us all.
🔭 What’s Next?
With Artemis missions aiming to return humans to the Moon and private companies racing toward Mars, 3D printing will be a vital part of the toolkit. Expect to see:
- Autonomous robotic printers building infrastructure before humans arrive
- Hybrid manufacturing systems combining CNC and additive tech
- AI-driven design optimization for space-grade components
✨ Final Thoughts
3D printing in space isn’t just a cool concept—it’s a necessity for the next generation of exploration. As we venture farther from Earth, the ability to create what we need, when we need it, will define our success. The stars are no longer the limit—they’re the next workshop.



Leave a comment